一个简单的(可能算劣质的)中文的模仿OpenAI的测试站:gpt.deepdialog.ai
OpenAI也是一定程度支持中文的,但是别太期待
后续正文还是先简单科普了OpenAI现在的功能
最后解析了OpenAI的一些Example的例子
给出了样例列表
大概一个星期之前,OpenAI“全面”开放了,因为之前的用户要先加入他们的等待列表,然后等待被选中。 不过现在,只要符合“一定条件”的用户,都可以直接登录并使用功能,每个人默认账号有一定的金额,可以对OpenAI的功能进行测试。
OpenAI提供的例子还是很多的,数了一下在这个提供了49个例子,通过这些例子可以学习到到底OpenAI现在可以做什么。
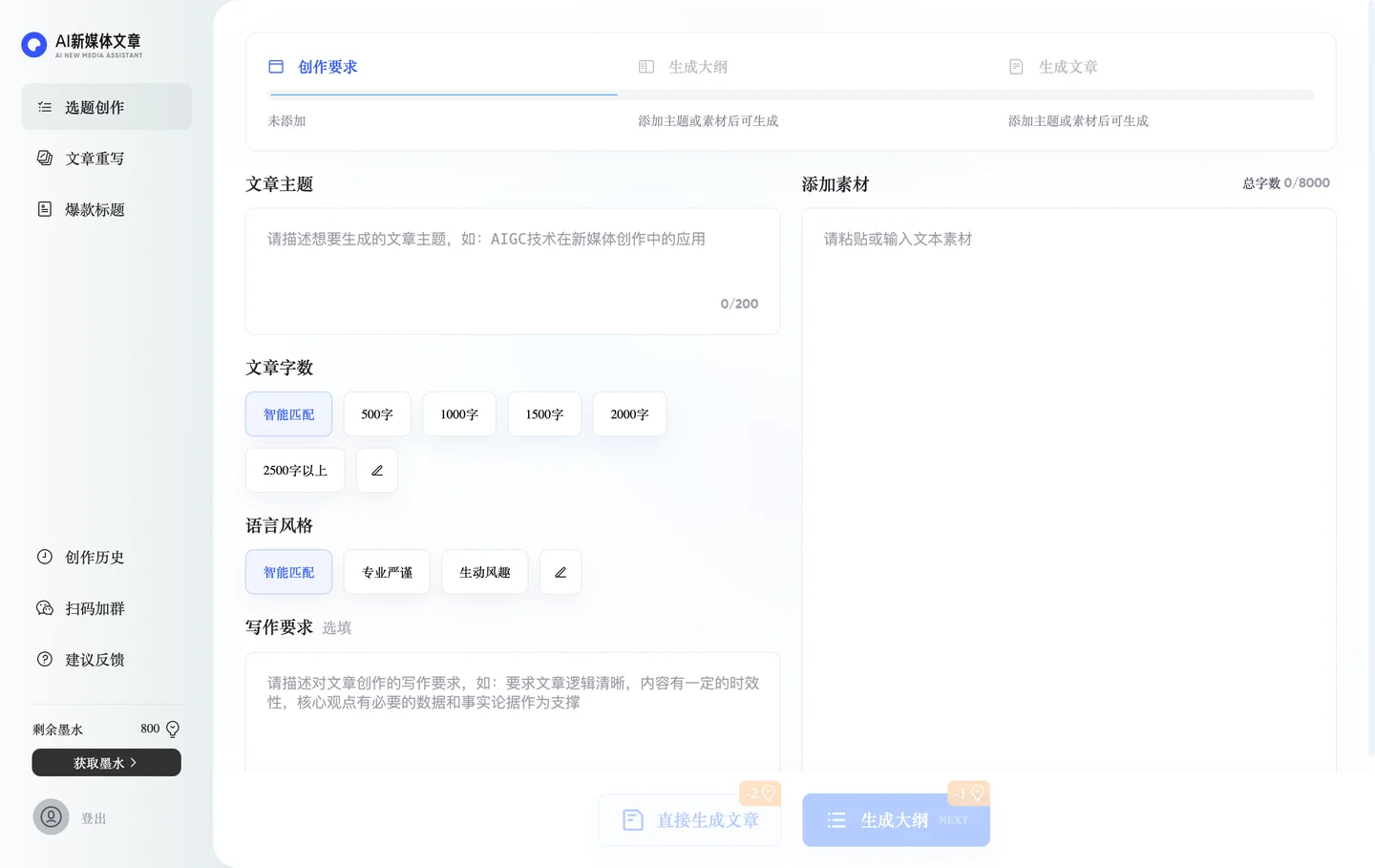
如果访问OpenAI有困难,或者只是想简单的感觉一下此类模型,作者模仿OpenAI,利用开源模型,仿造了一个中文版的OpenAI,地址是 gpt.deepdialog.ai
简单科普:
OpenAI提供了4个模型,代表不同的成本与费用/复杂度/完成不同难度大任务。已经不能简单的认为还是最开始的论文中的那个GPT-3了,肯定经过了更多优化、调试、测试或者后续训练。
不过本质上还是GPT类的生成模型。
此类生成模型解决问题依然可以认为主要依赖于“续写”。
我们可以认为自己在写试卷就是一种“续写”。
首先考试题目会通过一个简介(或者提示,Prompt)告诉我们你要做什么,例如:“请参考例句,把句子从第三人称改为第一人称”。
然后给你一个或多个(当然也可能没有)的例子,例如:“改写前:小明今天去买了一个冰淇淋;改写后:我今天去买了一个冰淇淋。”
在例句之后,你要给出的是你要通过这个功能提出的问题,例如你要把“小红今天出去骑车了”这句话改为第一人称,应该就如同例子一样,写作:“改写前:小红今天出去骑车了;”。
然后也要给算法一定的提示,写一个:“改写后:”,最终期待算法能帮助你继续“续写”,也就是完成这个功能。
整理来说,也就是说你要给算法提供的完整上下文类似:
请参考例句,把句子从第三人称改为第一人称 改写前:小明今天去买了一个冰淇淋;改写后:我今天去买了一个冰淇淋。 改写前:小红今天出去骑车了;改写后:
你希望算法通过阅读上面这段话(这段上下文),就能继续通过“续写”来输出正确的答案。
从另一个角度来说,研究深度学习的工程师们,“意外地”发现了类似GPT这样的生成模型可以达到这样的能力。
至少在部分应用上,可以达到某个准确率。
虽然GPT-3也发布了相当长的时间,但是显然OpenAI的很多功能依然可以说在测试中,也请不要期待它能多么的智能,人工智能,要能解决所有问题的人工智能,毕竟还有很长的路要走。
另外,OpenAI提到的能完成的任务(样例),它并不一定能完成的很好,尤其你要求很高的话。
OpenAI没列出的任务,它并不一定不能做,生成模式的这类算法的一个好处是,它带给了我们很多想象力,也许当你给了它足够的上下文和提出了合理的问题的时候,它刚好就能完成你的问题了呢。
我们通过连个OpenAI提供的样例来看它能完成的任务:
第一个,聊天:
OpenAI的介绍是,这是一个开放的AI助理,需要输入到算法的提示(Prompt)是这样的:
The following is a conversation with an AI assistant. The assistant is helpful, creative, clever, and very friendly. Human: Hello, who are you? AI: I am an AI created by OpenAI. How can I help you today? Human: I'd like to cancel my subscription. AI:
其中第一行“The following……”可以认为是我上面提到的,对于问题的提示。同时这里也相当于给了算法一个关于这个机器人能力的提示。理论上如果我们修改这个提示的内容,比如把对这个AI助理的介绍从“helpful, creative, clever, and very friendly.”,改为类似“useless and rude”,这样算法的输出结果就可能不同,因为输入的上下文不同,理论上算法就会根据内容得到类似的结果(如同人一样)。注意是“可能”不同,实际上,你可能并不觉得有什么区别。
第二行和第三行,可以认为是给算法的一个例子,或者提示,也就是告诉算法,你应该按照这样的格式给我输出结果。
第四行才是你的真正问题,也就是希望这个“AI助理”能回答的问题。
第五行的“AI:”是一个最后的提示,再次重申我要这样的输出格式。
第二个例子:
I am a highly intelligent question answering bot. If you ask me a question that is rooted in truth, I will give you the answer. If you ask me a question that is nonsense, trickery, or has no clear answer, I will respond with "Unknown".
Q: What is human life expectancy in the United States? A: Human life expectancy in the United States is 78 years.
Q: Who was president of the United States in 1955? A: Dwight D. Eisenhower was president of the United States in 1955.
Q: Which party did he belong to? A: He belonged to the Republican Party.
Q: What is the square root of banana? A: Unknown
Q: How does a telescope work? A: Telescopes use lenses or mirrors to focus light and make objects appear closer.
Q: Where were the 1992 Olympics held? A: The 1992 Olympics were held in Barcelona, Spain.
Q: How many squigs are in a bonk? A: Unknown
Q: Where is the Valley of Kings? A:
上面的例子和聊天类似,首先第一行“I am a……”给出了问题的描述。然后下面的“Q:……/A:……”的部分,主要是告诉算法应该如何回答问题,回答的格式是什么样。
最后的“Q: Where is the Valley of Kings?”才是真正的问题。
上面两个例子可以大体上看出OpenAI的一种回答问题的模式和感觉,其他的所有例子都是相似的。
这种解决问题的方法在GPT-3的原文中,被称为In-context learning。也就是算法通过上下文进行一部分“学习”,或者我们也可以认为是一种“模仿”。
附:
OpenAI的中文模仿现在提供的样例功能:
gpt.deepdialog.ai
聊天: 完成聊天对话
场景对话: 根据设定场景,完成对话,类似剧本续写
对联: 根据给出的对联上联,完成下联
关键词抽取: 实现针对文章的关键词抽取
文本摘要: 实现针对文章的摘要
文本分类: 根据给出的选项,对文章进行抽取
问答: 回答事实问题
汉译英: 实现英文到中文的翻译
英译汉: 实现中文到英文的翻译
推理关系: 判断前提和假设的矛盾、蕴含、中立关系
菜谱生成: 生成菜谱
虚假名言: 生成虚假的名人名言
作文续写: 给出作文题目,继续书写
小说续写: 给出小说章节的一部分,继续写作后面部分
OpenAI官网现在提供的样例功能:
Chat: Open ended conversation with an AI assistant.
Q&A: Answer questions based on existing knowledge.
Grammar correction: Corrects sentences into standard English.
Summarize for a 2nd grader: Translates difficult text into simpler concepts.
Natural language to OpenAI API: Create code to call to the OpenAI API using a natural language instruction.
Text to command: Translate text into programmatic commands.
English to French: Translates English text into French.
Natural language to Stripe API: Create code to call the Stripe API using natural language.
SQL translate: Translate natural language to SQL queries.
Parse unstructured data: Create tables from long form text
Classification: Classify items into categories via example.
Python to natural language: Explain a piece of Python code in human understandable language.
Movie to Emoji: Convert movie titles into emoji.
Calculate Time Complexity: Find the time complexity of a function.
Translate programming languages: Translate from one programming language to another
Advanced tweet classifier: Advanced sentiment detection for a piece of text.
Explain code: Explain a complicated piece of code.
Keywords: Extract keywords from a block of text.
Factual answering: Guide the model towards factual answering by showing it how to respond to questions that fall outside its knowledge base. Using a '?' to indicate a response to words and phrases that it doesn't know provides a natural response that seems to work better than more abstract replies.
Ad from product description: Turn a product description into ad copy.
Product name generator: Create product names from examples words. Influenced by a community prompt.
TL;DR summarization: Summarize text by adding a 'tl;dr:' to the end of a text passage. It shows that the API understands how to perform a number of tasks with no instructions.
Python bug fixer: Find and fix bugs in source code.
Spreadsheet generator: Create spreadsheets of various kinds of data. It's a long prompt but very versatile. Output can be copy+pasted into a text file and saved as a .csv with pipe separators.
JavaScript helper chatbot: Message-style bot that answers JavaScript questions
ML/AI language model tutor: Bot that answers questions about language models
Science fiction book list maker: Create a list of items for a given topic.
Tweet classifier: Basic sentiment detection for a piece of text.
Airport code extractor: Extract airport codes from text.
SQL request: Create simple SQL queries.
Extract contact information: Extract contact information from a block of text.
JavaScript to Python: Convert simple JavaScript expressions into Python.
Friend chat: Emulate a text message conversation.
Mood to color: Turn a text description into a color.
Write a Python docstring: An example of how to create a docstring for a given Python function. We specify the Python version, paste in the code, and then ask within a comment for a docstring, and give a characteristic beginning of a docstring (""").
Analogy maker: Create analogies. Modified from a community prompt to require fewer examples.
JavaScript one line function: Turn a JavaScript function into a one liner.
Micro horror story creator: Creates two to three sentence short horror stories from a topic input.
Third-person converter: Converts first-person POV to the third-person. This is modified from a community prompt to use fewer examples.
Notes to summary: Turn meeting notes into a summary.
VR fitness idea generator: Create ideas for fitness and virtual reality games.
ESRB rating: Categorize text based upon ESRB ratings.
Essay outline: Generate an outline for a research topic.
Recipe generator: Create a recipe from a list of ingredients.
Marv the sarcastic chat bot: Marv is a factual chatbot that is also sarcastic.
Turn by turn directions: Convert natural language to turn-by-turn directions.
Restaurant review creator: Turn a few words into a restaurant review.
Create study notes: Provide a topic and get study notes.